
Archive Of Unremarkable Radiological Studies Left Hand XRay Stepwards
The locations of the epiphyses of the phalanges and metacarpals and the radiographic characteristics of the nutrient artery canals are key practical aspects of the radiographic anatomy of the hand. The phalangeal and metacarpal epiphyses are differently located, and even among the metacarpals, the location of the growth centers is not uniform.

Image
We're breaking down positioning criteria for PA & Oblique hand x-rays.Subscribe for more videos like this: https://www.youtube.com/user/TopicsInRadiography?s.

Image
Place arm on the table with elbow bent. Ideally, upper arm, elbow, and forearm are all resting on the table. Position of part: Hand centered palm down flat, fingers separated. The central ray should be perpendicular to the image receptor at 3rd MCP joint. Central ray: Perpendicular to the image receptor at 3rd MCP joint.

Hand xray. Causes, symptoms, treatment Hand xray
Part Position: Center the image receptor to the MCP joints, and adjust it so that its midline is parallel with the long axis of the hand and forearm. With the patient relaxing the digits to maintain the natural arch of the hand, arrange the digits so that they are perfectly superimposed. Have the patient hold the thumb parallel with the IR, or.
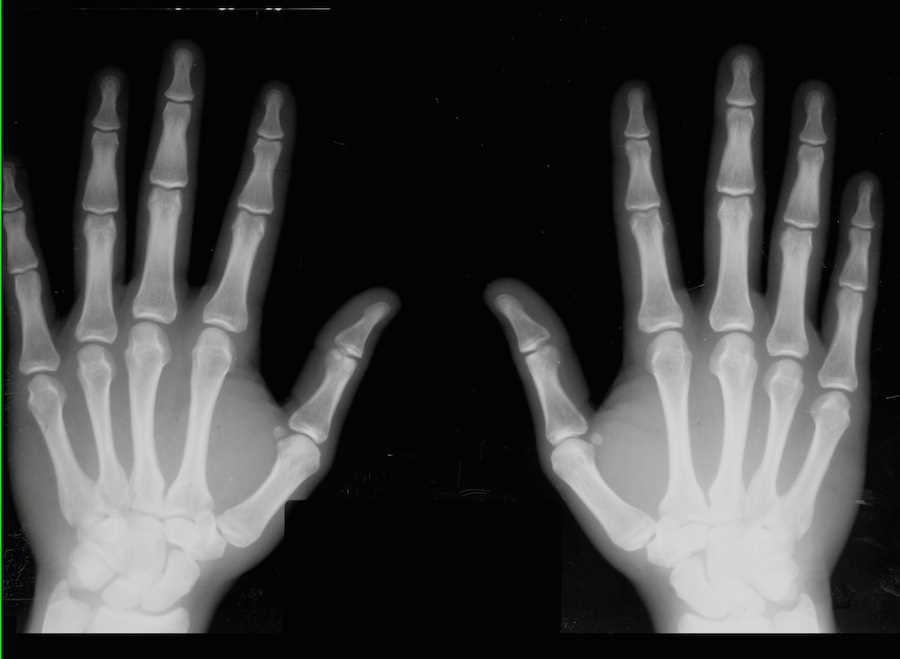
Normal Hands on Xray X Rays Case Studies CTisus CT Scanning
Finger injuries visible on X-ray include bone fractures, dislocations and avulsions. The hand comprises the metacarpal and phalangeal bones. Fractures and dislocations are usually straightforward to identify, so long as the potentially injured bone is fully visible in 2 planes. Finger joints commonly dislocate and are susceptible to avulsion.

Wrist XRay 2 a photo on Flickriver
Indications. The PA hand view is requested for diagnosing a variety of clinical indications such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, suspected fracture or dislocation and localizing foreign bodies. This view complements the ball-catcher view as it is particularly useful for diagnosing early signs of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
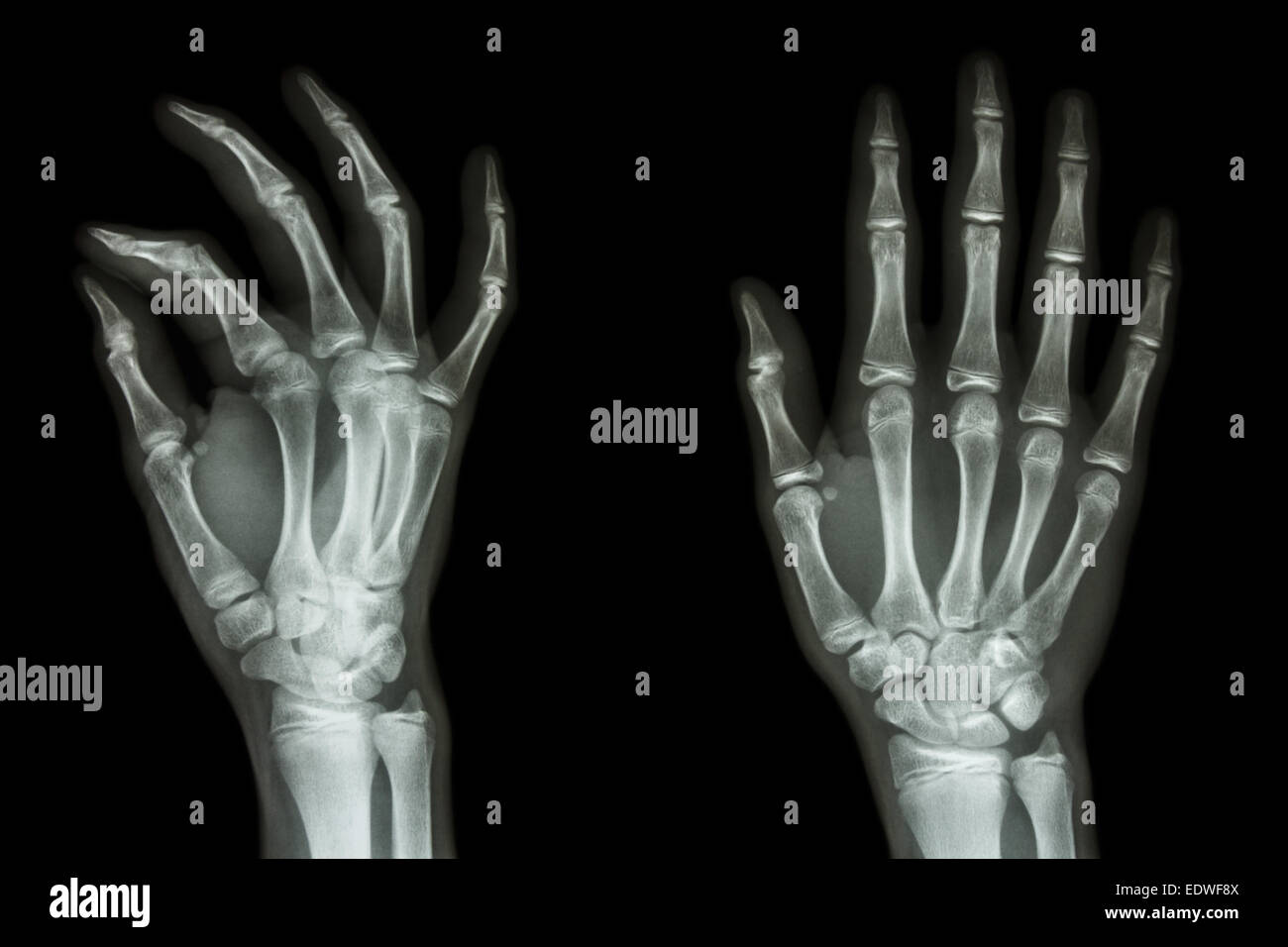
film xray Hand AP/Oblique show normal human's hand Stock Photo Alamy
Scout view of wrist and hand. Lines # 1-11 indicate position of sections (1.5 mm thick) in the following CT series. Arrows ←, →, and ↔ in the legends indicate that a structure can be seen on a previous or following section, or both. Trapezium. Trapezoid bone. Capitate bone. Hamate bone. Scaphoid bone. Lunate bone.

Not Your Typical Wrist Pain — EM Curious
extends from the radiocarpal joint to the tips of fingers. similar series. wrist series. distal radius and ulna, carpals and proximal metacarpals. scaphoid series. wrist series plus two additional scaphoid views. thumb series. just for looking at the thumb. both hands.

Plain Xray of right wrist anteriorposterior view and lateral view.... Download Scientific
For this reason it is advisable to refer to the digits by names given to them rather than by number. From the radial to the ulnar aspect of the hand, they are named as follows: thumb. index finger. middle finger or long finger. ring finger. little finger. In the standard anatomical position, the hand is flat and supinated with the fingers spread.

Xray lateral view of adult hand Stock Photo Alamy
no superimposition of triquetrum, lunate, or pisiform. Ulnar/radial deviation view. Positioning. patient. shoulder abducted 90° + elbow flexed 90° + forearm pronated + hand ulnarly vs. radially deviated. beam. aim at scaphoid. Indications. ulnar deviation = lateral wrist + scaphoid fracture.
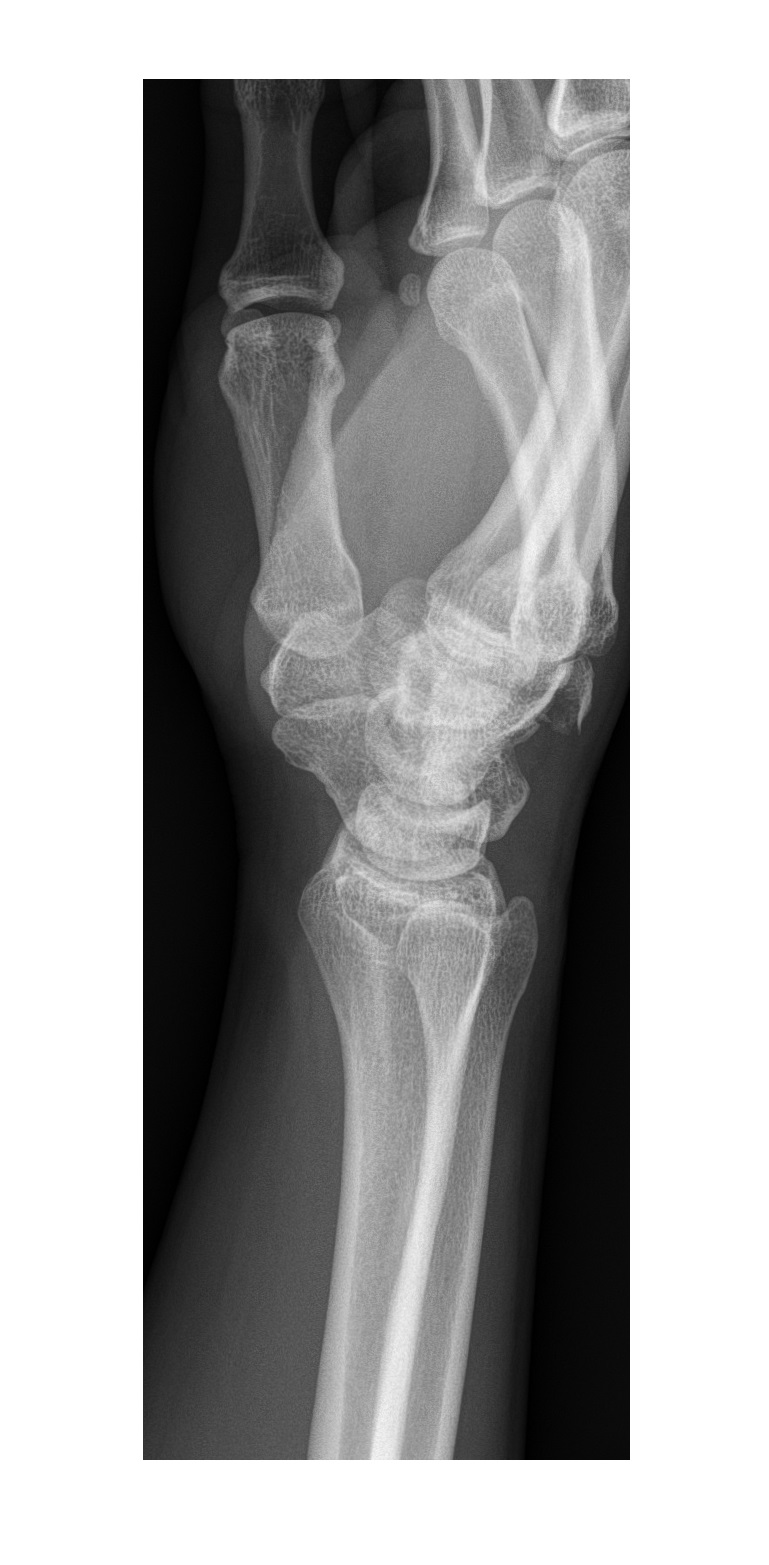
Hand xray lateral Emergucate
A hand X-ray (radiograph) is a test that creates a picture of the inside of your hand. The picture shows the inner structure ( anatomy) of your hand in black and white. Calcium in your bones absorbs more radiation, so your bones appear white on the X-ray. Soft tissues, such as muscle, fat and organs, absorb less radiation, so they appear.
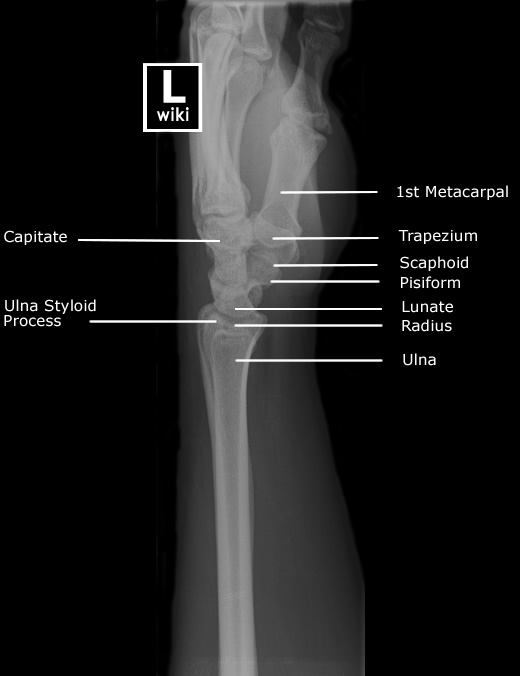
Wrist Radiographic Anatomy wikiRadiography
FIGURE 5-1. Three standard views of the standard radiographic examination of the traumatized hand: A, PA, B, pronation oblique, and C, lateral. When the injury is confined to a single digit, a phalanx, greater detail and a sharper image are obtained by limiting the exposure to the digit in question as shown in Figure 5-2 of left index finger.

Hand xray. Causes, symptoms, treatment Hand xray
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. The bilateral PA view is merely a single film that includes both hands, side by side. Although convenient, recent research has shown that the distortion due to divergent ray when imaging bilaterally can impact diagnosis and x-raying the hands individually is preferred at a minimal dose increase 1.

Lateral radiograph of the right wrist The BMJ
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. The hand series consists of posteroanterior, oblique, and lateral projections. Although additional radiographs can be taken for specific indications. The series primarily examines the radiocarpal and distal radioulnar joints, the carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges.
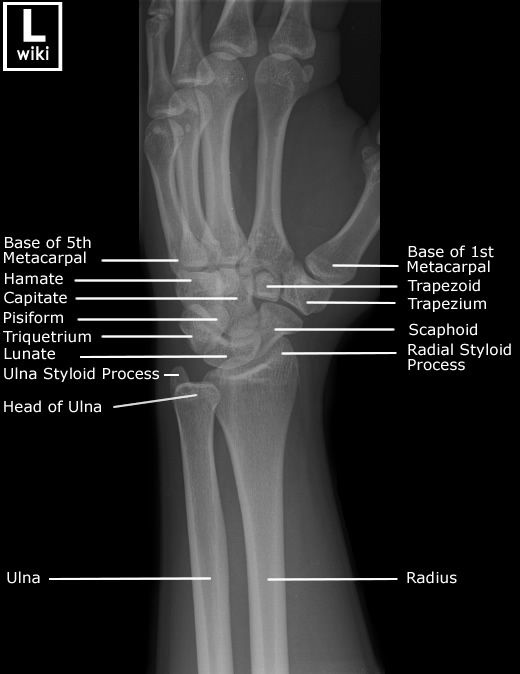
Wrist Radiographic Anatomy wikiRadiography
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. The finger lateral view is a standard projection for radiographic assessment of the fingers; it is one of three views of the finger series. it is divided into: lateral index and middle fingers. lateral of ring and little fingers.
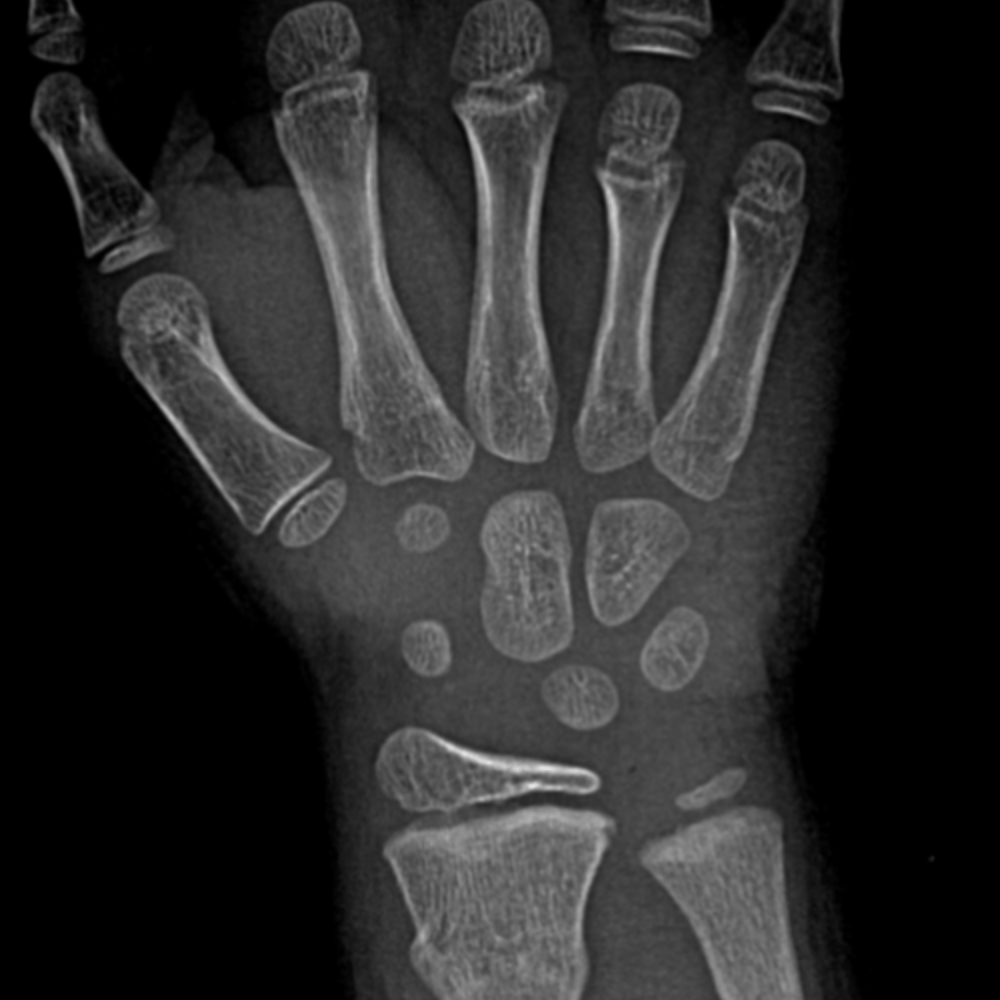
Interactive Pediatric Wrist & Hand Radiograph Cases
Radiography. Imaging evaluation of the hand and fingers often begins with conventional radiographs, especially in the setting of acute trauma for suspected fracture or dislocation. Radiographs are usually adequate to delineate the specific osseous abnormality following trauma. Evaluation in other clinical settings such as suspected arthritis.