RADICULOPATIA CERVICAL O QUE VOCÊ PRECISA SABER Head & Neck
INTRODUCTION. Cervical radiculopathy (CR) is a common pain syndrome characterized by sensorimotor deficits due to cervical nerve root compression and inflammation [].In C5 or C6 radiculopathy, the proximal shoulder girdle muscles are commonly involved and it may be difficult for the patients to raise their shoulder [].The diagnosis of CR is based on clinical findings, imaging studies, and.
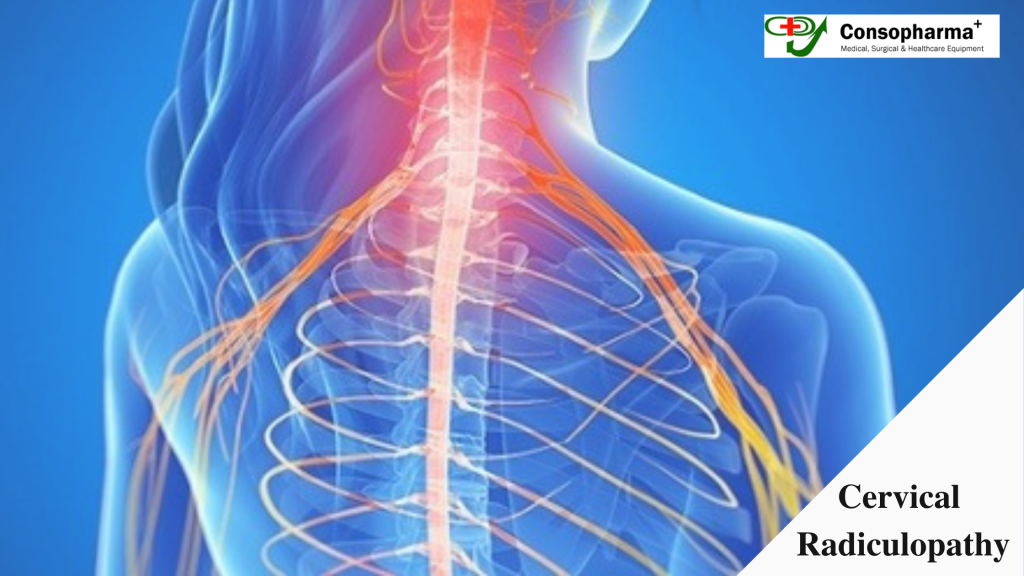
Cervical Radiculopathy Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment CONSOPHARMA+
Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a "pinched nerve," occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal cord. This may cause pain that radiates into the shoulder and/or arm, as well as muscle weakness and numbness. Cervical radiculopathy is often caused by "wear and tear" changes that occur.

Finding Relief Cervical Radiculopathy and Chiropractic Care
When a nerve in the cervical spine (neck) is irritated or damaged and causes pain and/or neurological symptoms, doctors call this condition - cervical radiculopathy. The nerves in the spine exit the spinal column through holes in the bones of the spine (vertebrae) from the right and left sides. The nerves exiting the spinal canal (nerve roots) are numbered from 1 to 8, based on the same.

slipped disc upper neck Dorothy Cameron
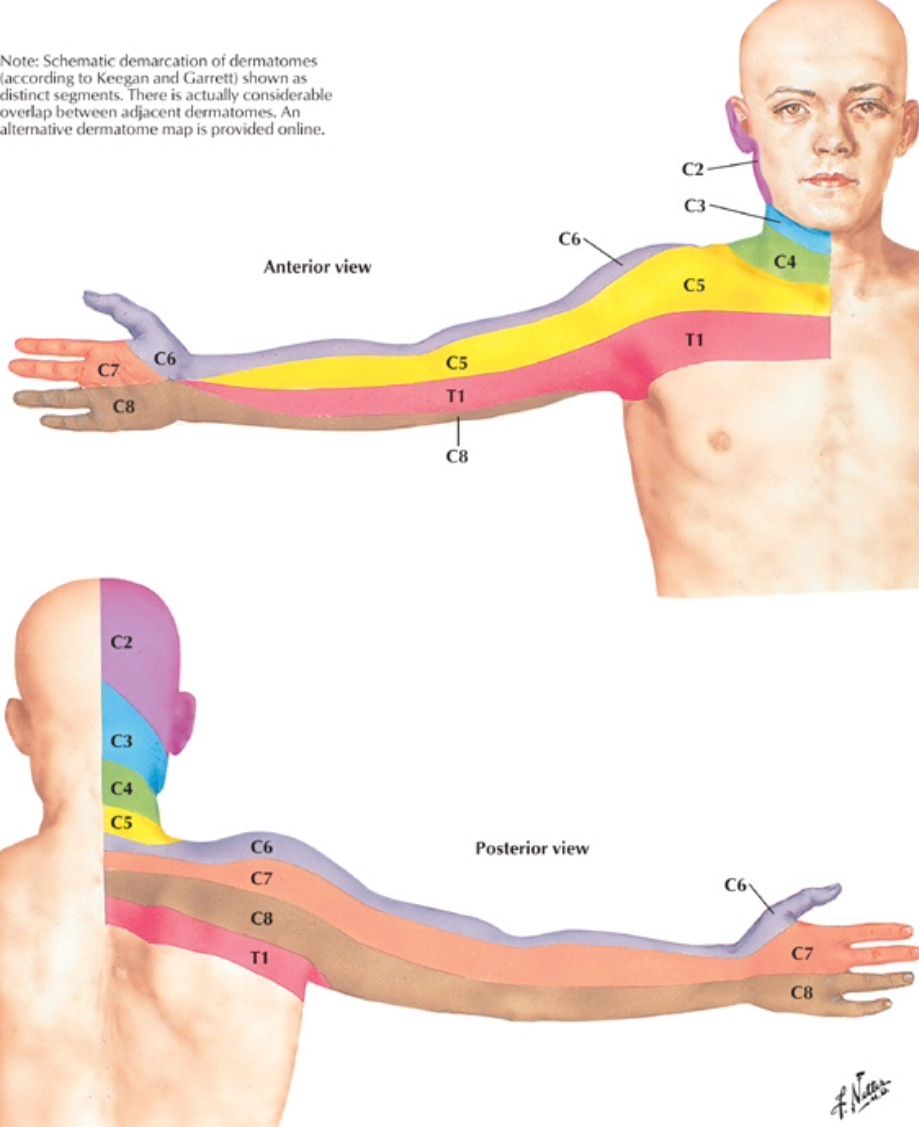
C6 spinal nerve. In between C5-C6, the C6 spinal nerve exits the spinal cord through a small bony opening on the left and right sides of the spinal canal called the intervertebral foramen. This C6 nerve has a sensory root and a motor root. The C6 dermatome is an area of skin that receives sensations through the C6 nerve.
Saiba mais sobre Radiculopatia Cervical Dr. Daniel Souto
Record the duration and nature of symptoms and treatments that have been attempted so far, and be alert for red flag conditions. There are several common sensory presentations seen in patients with cervical radiculopathy: Severe pain radiating from the neck down the arm. Intrascapular pain. Paresthesia and dysesthesia in a dermatome pattern.
Cervical Radiculopathy Spine Orthobullets
Radiculopathy is caused by a pinched nerve in your spine. More specifically, it happens when one of your nerve roots (where your nerves join your spinal column) is compressed or irritated. You might see it referred to as radiculitis. Radiculopathy will cause the area around your pinched nerve to feel painful, numb or tingly.

C5 C6 Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Stretches & Exercises
Cervical radiculopathy is a condition that affects the nerves or nerve roots in the neck, causing pain, numbness, or weakness in the upper extremities. This book chapter provides an overview of the anatomy, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of cervical radiculopathy, with references to relevant research articles. Learn more about this common spinal disorder and how to manage it.
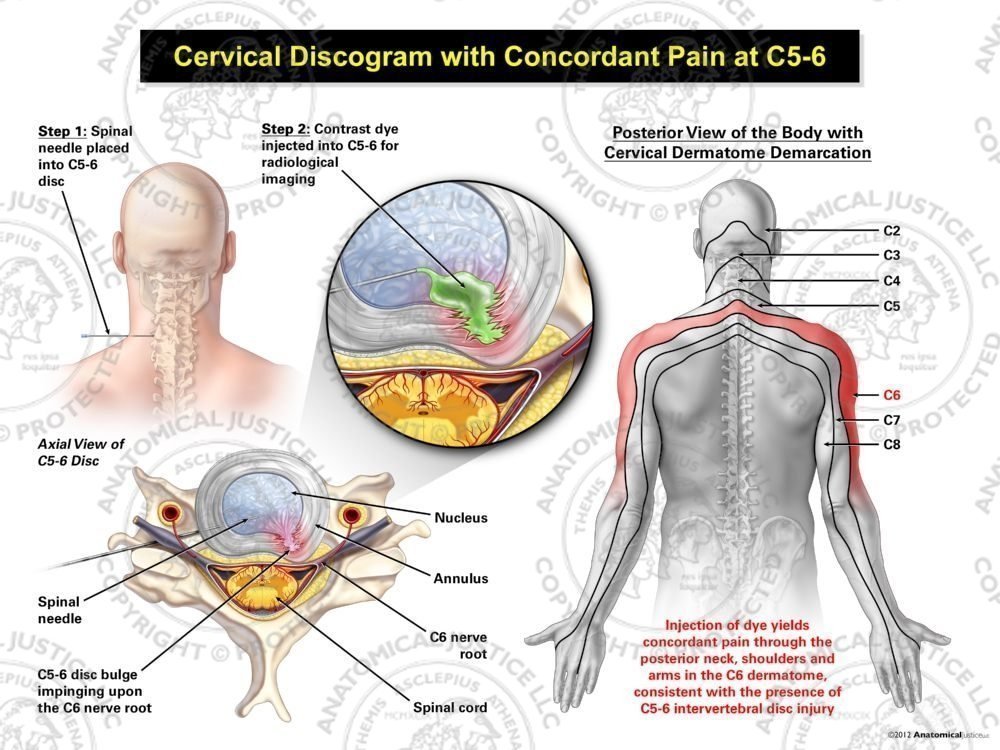
Male Left Cervical Discogram with Concordant Pain at C56
The main symptom of cervical radiculopathy is pain that spreads into the arm, neck, chest, upper back and/or shoulders. Often, this affects just one side of your body. Sensory issues, such as.

cervical spondylosis rosh Google Search Cervical radiculopathy
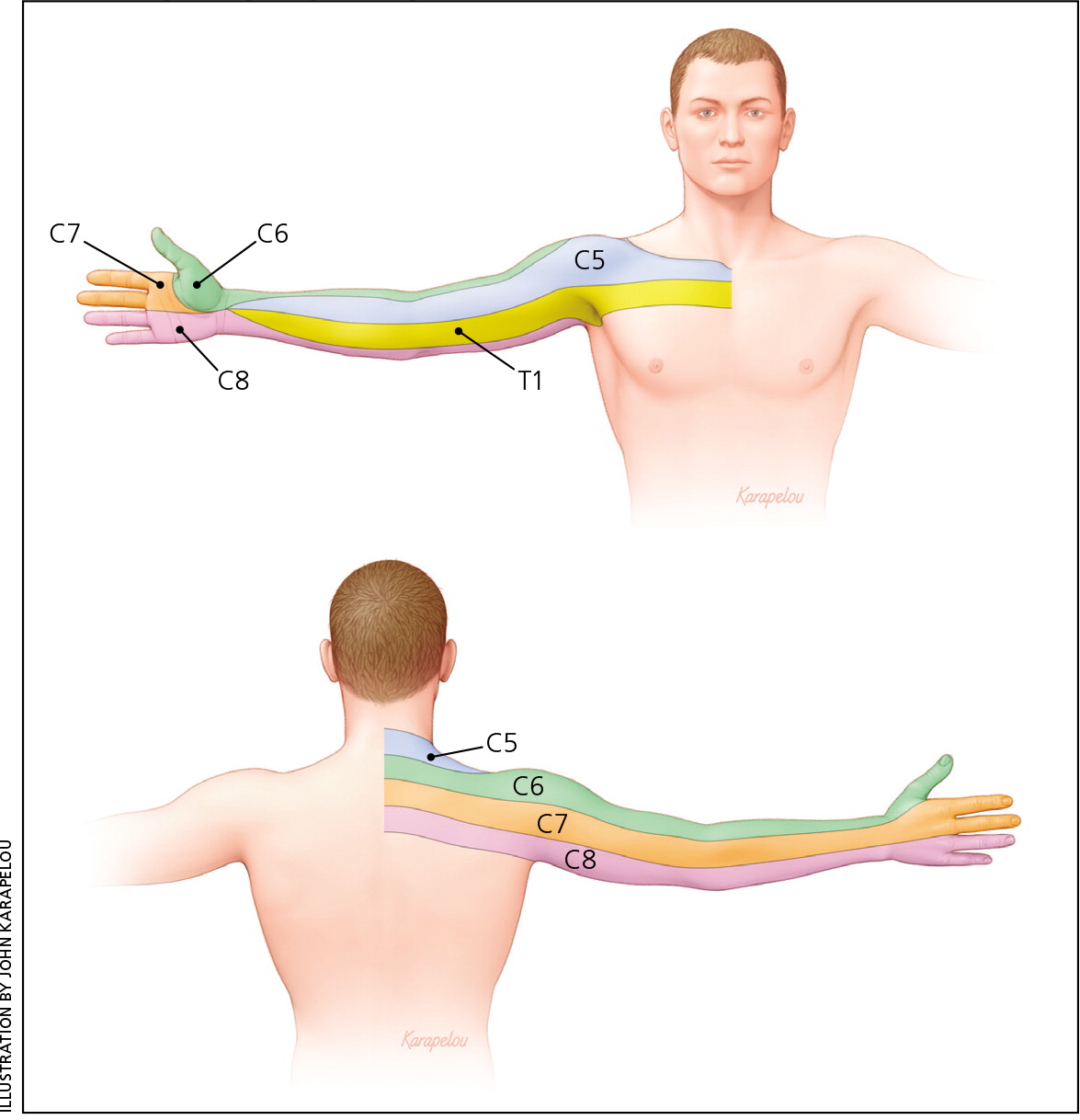
Pain on supra-scapular areas are associated with C5 or C6 radiculopathies, interscapular and infra-scapular pains are considered to be mainly from C7 and C8 radiculpathy, respectively. C2-4 radiculopathy is not common. Patients often complain of occipital or temporal pain that extends to the back of the ear or side of the neck.

Cervical radiculopathy infographic Pain in the Neck
Similarly, a disc herniation at the C5/6 level will lead to C6 nerve pinching or radiculopathy. The cervical spine consists of 7 bones or vertebrae along with 8 nerves or nerve roots. Cervical radiculopathy is a neurologic condition characterized by dysfunction of a cervical spinal nerve, the roots of the nerve, or both..

St. Louis Cervical Radiculopathy Neck Pain Car Accident Injury St
C5 pain occurs in the shoulder and radiates down the ventral arm to below the elbow. C6 radiculopathy is associated with pain down the superior lateral aspect of the arm into the first two digits. Commonly, there is overlap in the pain presentation of C6 radiculopathy and carpal tunnel syndrome. In carpal tunnel syndrome, patients often report.

What Is C5 C6 Radiculopathy? What Causes Cervical Radiculopathy? Dr
The primary pathology of pain in the shoulder region may not always be related to rotator cuff lesions. Cervical region pathologies can also cause pain complaints on the shoulder and arm [ 3 - 5 ]. Cervical pain, which is among the causes of shoulder pain, is seen at a significant frequency of 5% [ 6 ]. When the frequency of neck-shoulder.

Estudio de Radiculopatía cervical
C5. Dolor en el cuello, el hombro y la cara dorsal del antebrazo con parestesias y entumecimiento que afectan esta última área. C6. Dolor en el borde del trapecio y en la punta del hombro, que a menudo irradia hasta el pulgar, con parestesias y compromiso sensitivo en las mismas áreas. Debilidad del bíceps. Disminución de los reflejos.
Nonoperative Management of Cervical Radiculopathy AAFP
C6 radiculopathy. Tingling, numbness, and/or pain may radiate through the arm and into the second digit (index finger). Weakness may occur in the front of the upper arm (biceps) or wrist. See All About the C5-C6 Spinal Motion Segment. C7 radiculopathy. Tingling, numbness, and/or pain may be felt down the arm and into the middle finger.

Cervical Radiculopathy
C5 Radiculopathy: Primary innervation of the deltoid and biceps is from the C5 root with secondary innervation from the C6 root. Sensory NCS can not reliably assess the C5 nerve root. If the rhomboids show EMG changes on the exam, the C5 root is probably affected as the C5 root primarily innervates it with a small contribution from the C4 root.

Radiculopatia Cervical Causas, Sintomas e Tratamento
Results: According to our results, C 5 root compression (12.3%), C 6 root compression (41.5%), UTRC (44.6%) were detected. There was no difference between the groups regarding the Hawkins and Neer tests. The Yergason and Jobe tests were statistically higher in patients without UTRC. In the shoulder MRIs, the rate of subscapular muscle tear was.