
What Comes After Trigonometry? 17 Most Correct Answers
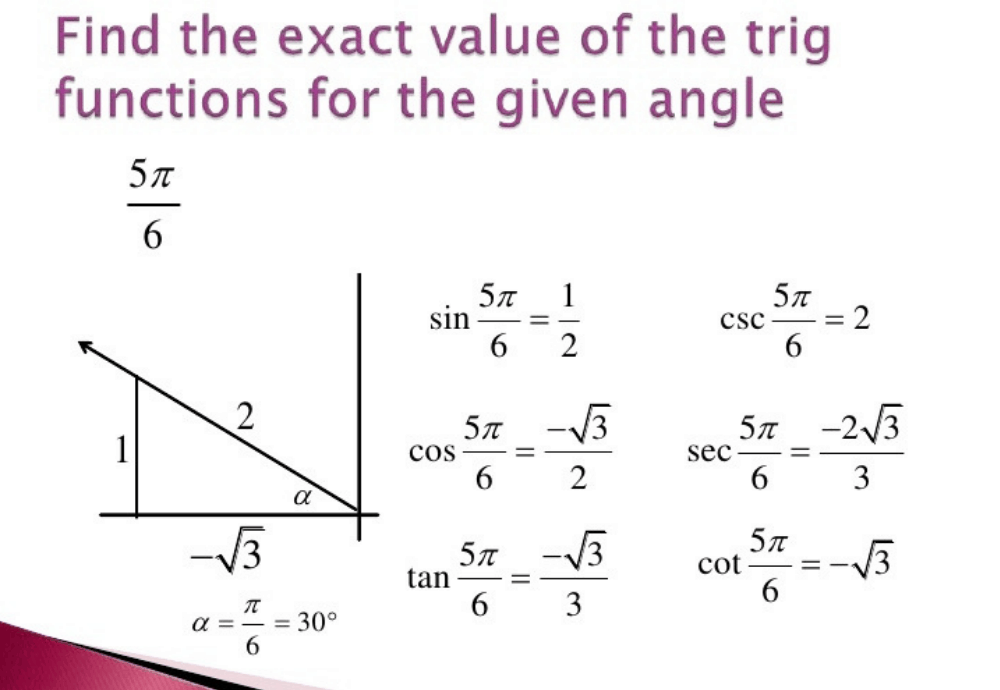
cos x - cos y = -2 sin( (x - y)/2 ) sin( (x + y)/2 ) Trig Table of Common Angles; angle 0 30 45 60 90; sin ^2 (a) 0/4 : 1/4 : 2/4 : 3/4 : 4/4 : cos ^2 (a) 4/4 : 3/4 : 2/4 : 1/4 : 0/4 : tan ^2 (a) 0/4 : 1/3 : 2/2 : 3/1 : 4/0 ; Given Triangle abc, with angles A,B,C; a is opposite to A, b opposite B, c opposite C:

sin cos tan formulas
Purplemath What is an identity? In mathematics, an "identity" is an equation which is always true, regardless of the specific value of a given variable. An identity can be "trivially" true, such as the equation x = x or an identity can be usefully true, such as the Pythagorean Theorem's a2 + b2 = c2 MathHelp.com Need a custom math course?

Contoh Soal Matematika Sin Cos Tan Berbagi Contoh Soal Riset
The basic relationship between the sine and cosine is given by the Pythagorean identity: where means and means This can be viewed as a version of the Pythagorean theorem, and follows from the equation for the unit circle.

How to get sin & cos in an easy way (Hand) YouTube
Want to learn more about the law of cosines? Check out this video. Practice set 1: Solving triangles using the law of sines This law is useful for finding a missing angle when given an angle and two sides, or for finding a missing side when given two angles and one side. Example 1: Finding a missing side Let's find A C in the following triangle:
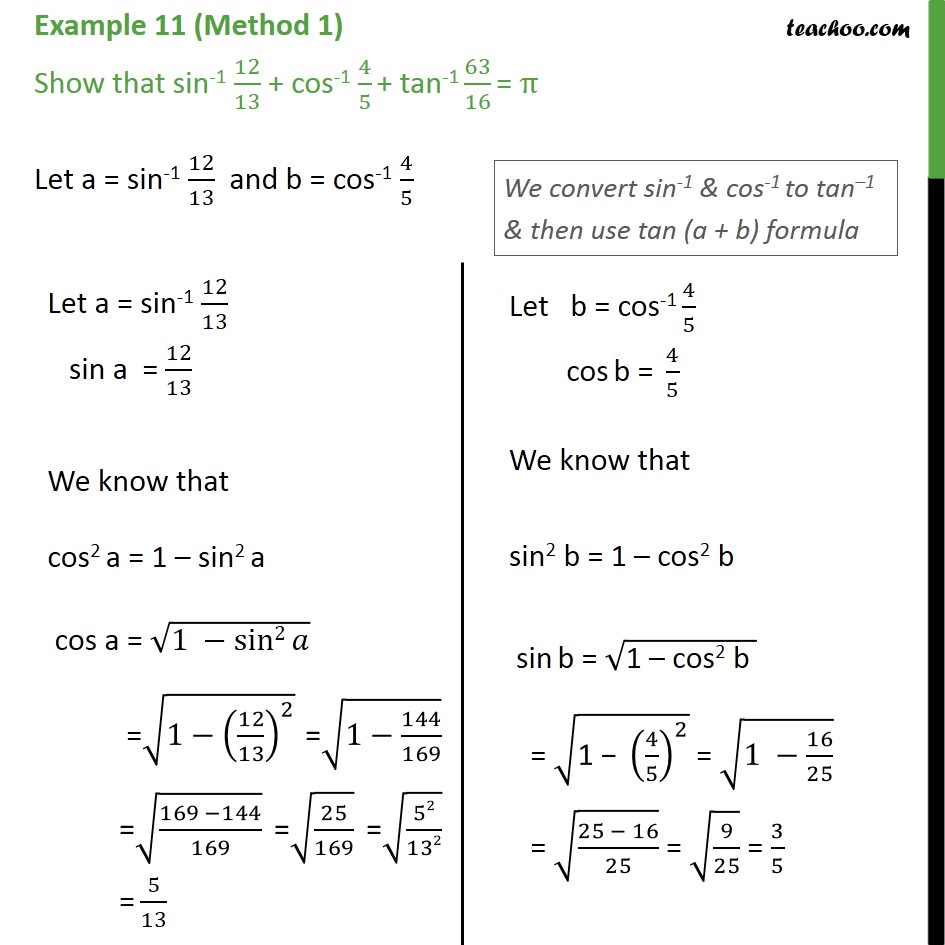
Example 11 Show sin1 12/13 + cos1 4/5 + tan1 63/16 = pi
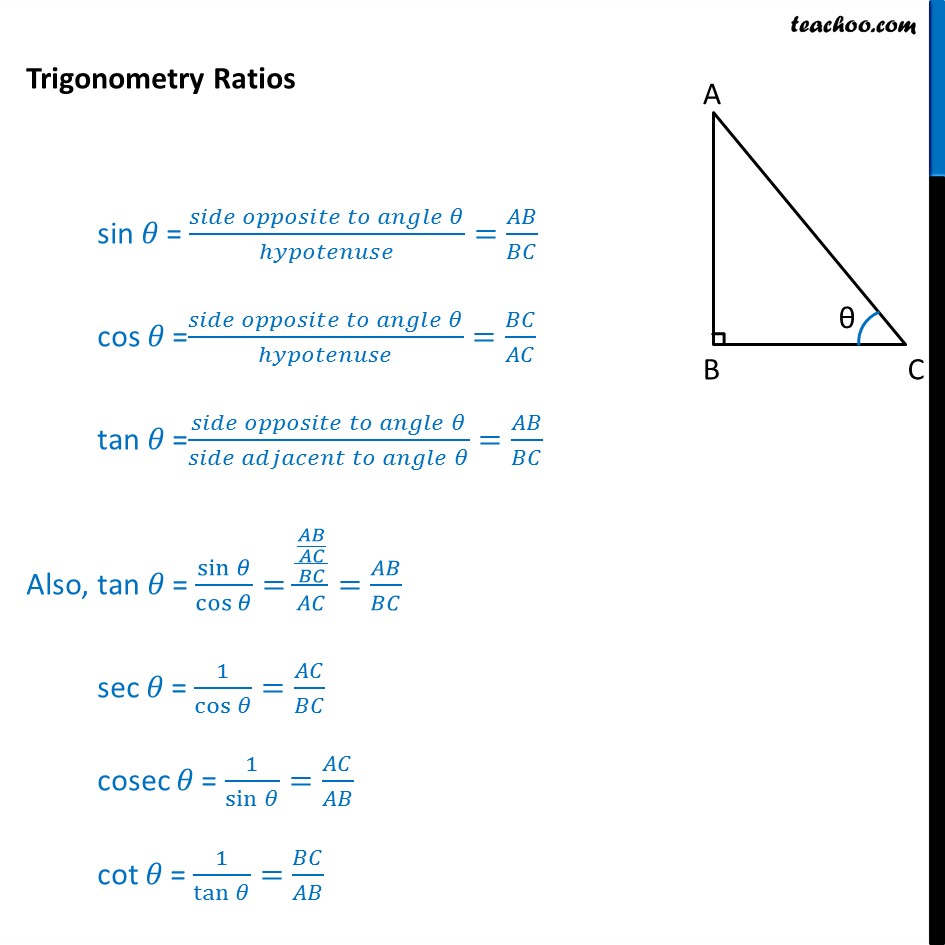
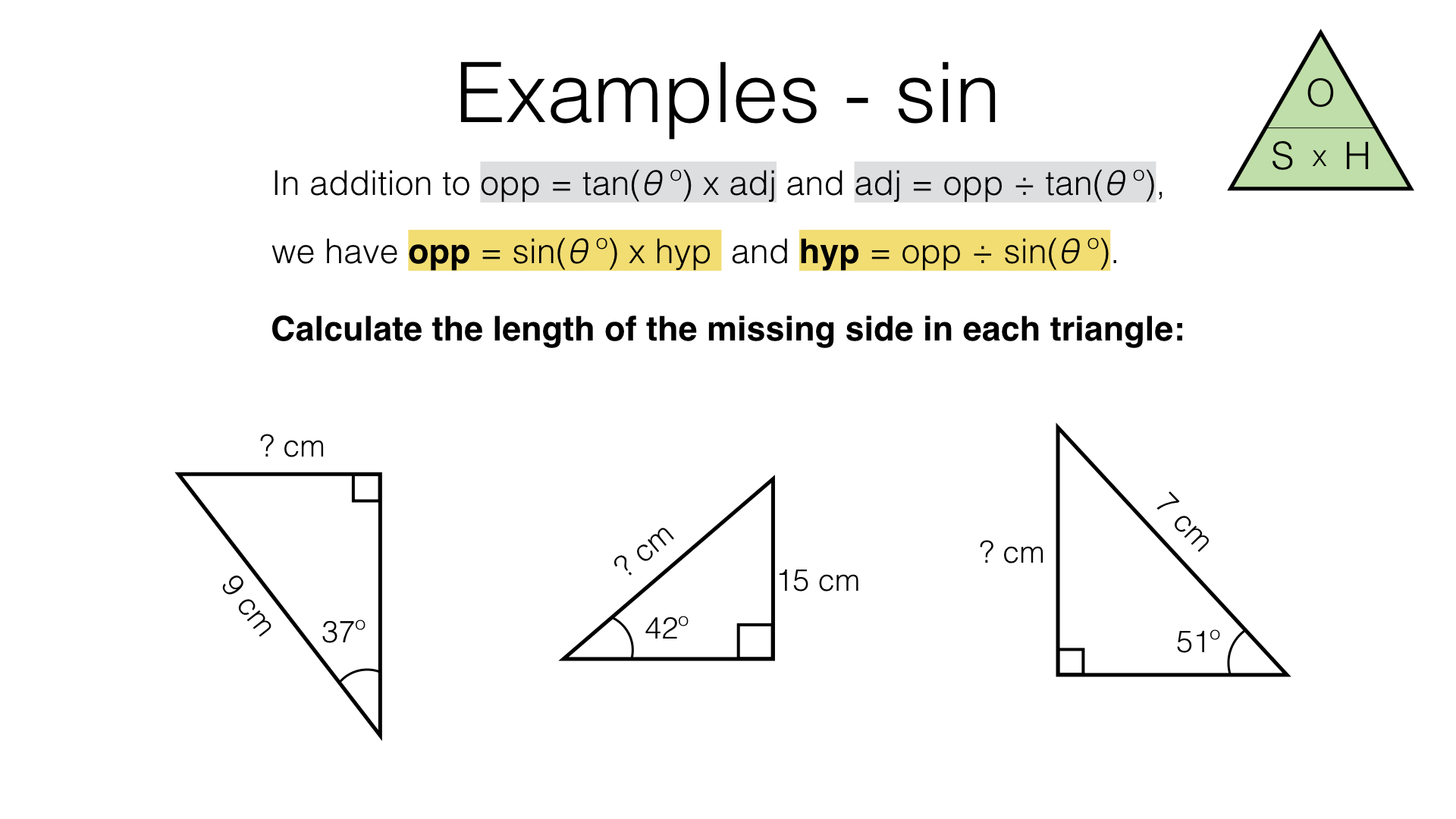
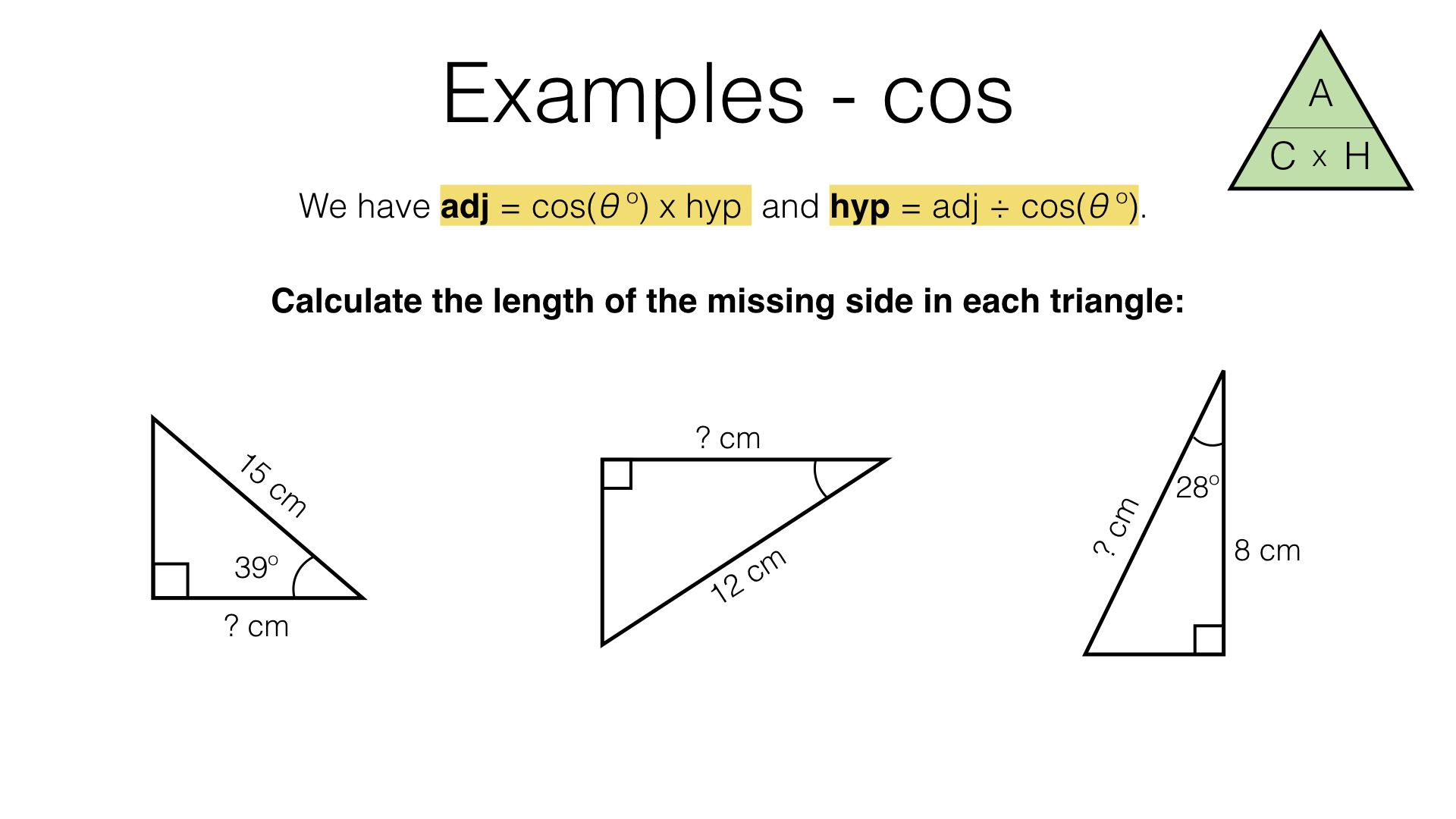
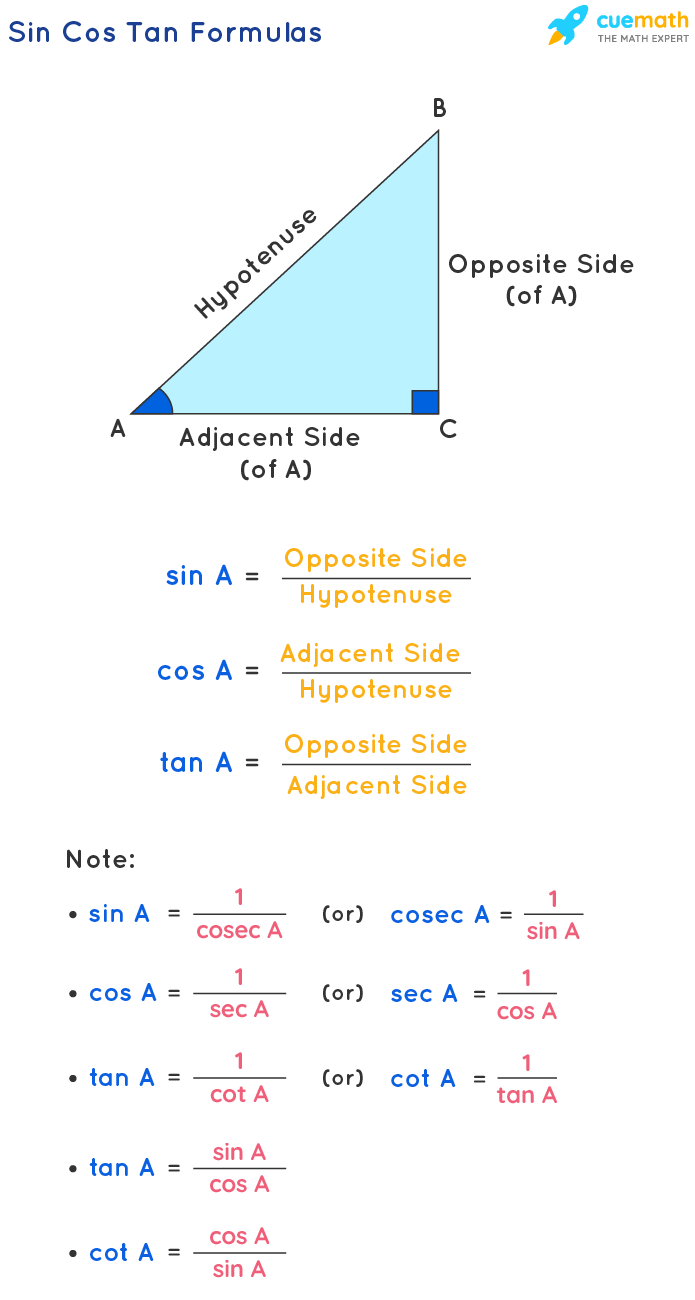
Three trigonometric ratios Trigonometry involves three ratios - sine, cosine and tangent which are abbreviated to \ (\sin\), \ (\cos\) and \ (\tan\). The three ratios are calculated by.
What are sin cos tan? Chapter 8 Class 10 Trignometric Ratios
Free math problem solver answers your trigonometry homework questions with step-by-step explanations.
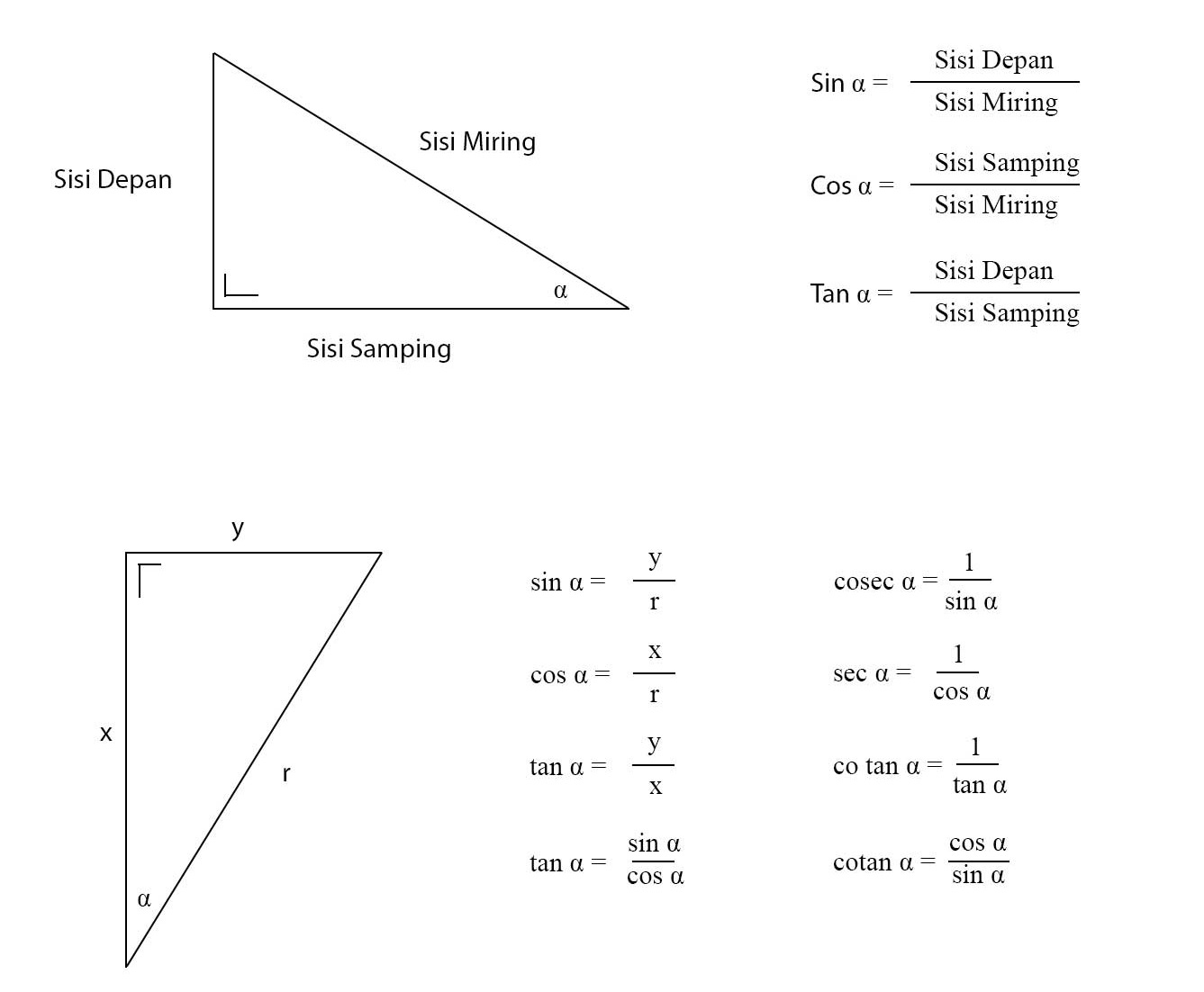
Belajar Sin Cos Tan Rumus Dengan Mudah Panduan Lengkap Untuk Pemula
where e is the base of the natural logarithm, i is the imaginary unit, and cos and sin are the trigonometric functions cosine and sine respectively. This complex exponential function is sometimes denoted cis x ("cosine plus i sine"). The formula is still valid if x is a complex number, and is also called Euler's formula in this more general case.
Trigonometric Pythagorean Identity, extended Florians Blog Simple
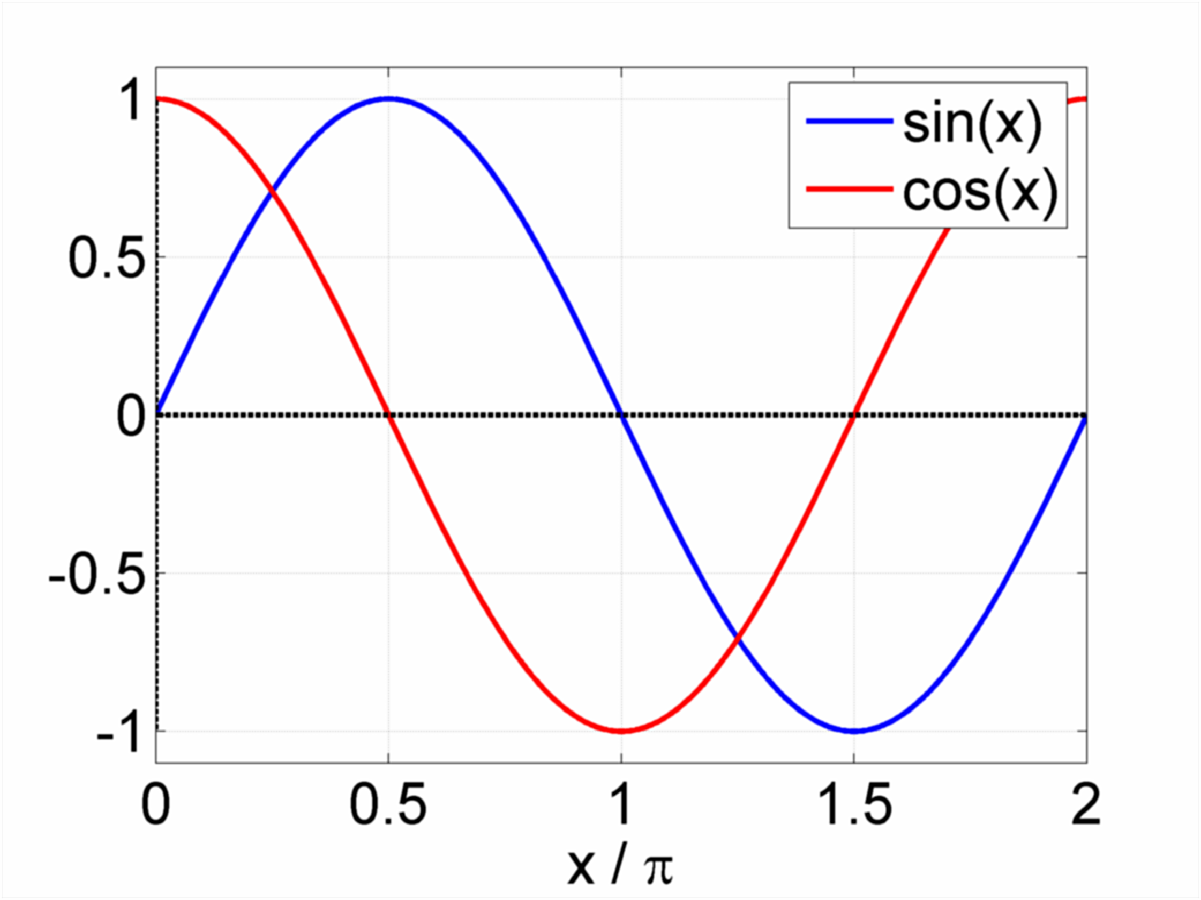
Sines Cosines Tangents Cotangents Pythagorean theorem Calculus Trigonometric substitution Integrals ( inverse functions) Derivatives v t e In mathematics, sine and cosine are trigonometric functions of an angle.

Trudiogmor Sin Cos Relation Table
Sines Cosines Tangents Cotangents Pythagorean theorem Calculus Trigonometric substitution Integrals ( inverse functions) Derivatives v t e Basis of trigonometry: if two right triangles have equal acute angles, they are similar, so their corresponding side lengths are proportional.
MATH ONLINE sin cos 2
GCSE Trigonometry - Intermediate & Higher tier - WJEC Sin, cos and tan Trigonometric relationships are very important in the construction and planning industry and allow precise calculation of.
Trigonometry Questions Sin Cos Tan
cis is a mathematical notation defined by cis x = cos x + i sin x, [nb 1] where cos is the cosine function, i is the imaginary unit and sin is the sine function. x is the argument of the complex number (angle between line to point and x-axis in polar form ).
Trigonometry Sin Cos Tan Solver
When we divide Sine by Cosine we get: sin (θ) cos (θ) = Opposite/Hypotenuse Adjacent/Hypotenuse = Opposite Adjacent = tan (θ) So we can say: tan (θ) = sin (θ) cos (θ) That is our first Trigonometric Identity. Cosecant, Secant and Cotangent We can also divide "the other way around" (such as Adjacent/Opposite instead of Opposite/Adjacent ):

sin cos tan uitleg overstaand en aanliggend YouTube
4 Answers Sorted by: 3 In Complex Analysis, we define sin z = z − z3 3! + z5 5! − ⋯ and cos z = 1 − z2 2! + z4 4! − ⋯ sin z = z − z 3 3! + z 5 5! − ⋯ and cos z = 1 − z 2 2! + z 4 4! − ⋯ In particular sin i = i − i3 3! + i5 5! − ⋯ = i ×(1 + 1 3! + 1 5! + ⋯) = sinh(1)i. sin i = i − i 3 3! + i 5 5! − ⋯ = i × ( 1 + 1 3! + 1 5! + ⋯) = sinh ( 1) i.
How To Calculate Sin Haiper
De nition (Cosine and sine). Given a point on the unit circle, at a counter-clockwise angle from the positive x-axis, cos is the x-coordinate of the point. sin is the y-coordinate of the point. The picture of the unit circle and these coordinates looks like this:

Misc 4 Prove (cos x cos y)2 + (sin x sin y)2 Chapter 3
Trigonometry involves three ratios - sine, cosine and tangent which are abbreviated to \(\sin\), \(\cos\) and \(\tan\). The three ratios can be found by calculating the ratio of two sides of a.
Sin Cos Tan Triangle Calculator Cheapest Wholesalers, Save 52 jlcatj
Trigonometry Formulas In Trigonometry, different types of problems can be solved using trigonometry formulas. These problems may include trigonometric ratios (sin, cos, tan, sec, cosec and cot), Pythagorean identities, product identities, etc.